How to Reset the Password or SSH Key on a Linux based VM in Rumble Cloud¶
Rumble Cloud does not have special access to reset a user's password or SSH key. However, since a VM behaves like a normal server, standard processes can be used to perform a password reset if such a process exists for your operating system.
This guide presents an example using Ubuntu 24.04, but the same process will be similar for most Linux distributions, and also for similar operating systems such as BSD-based derivatives.
Steps to reset a password or SSH key¶
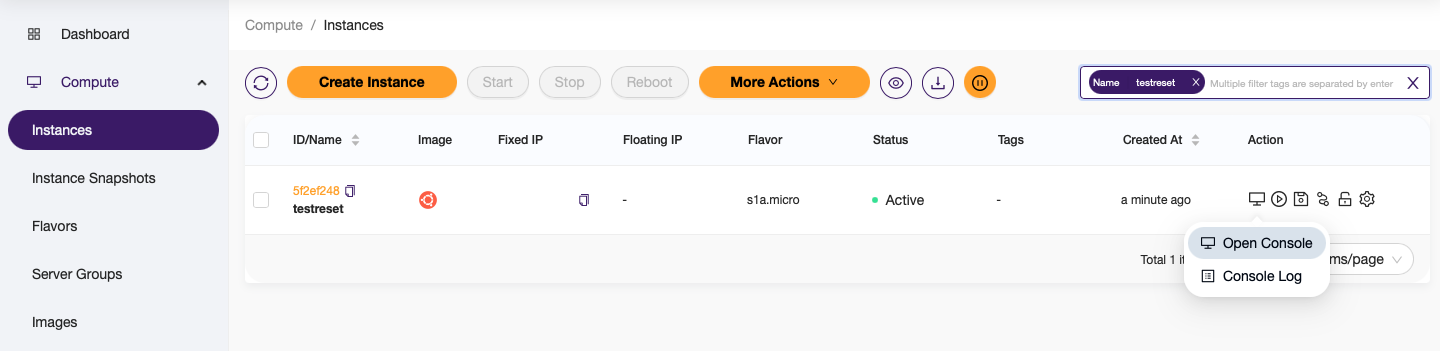
1. Log in to the console¶
Open the console for your VM from the Rumble Cloud dashboard.
2. Prepare your console window¶
Resize your browser window so you can easily access the "Send CtrlAltDel" button in the top-right corner.
Click inside the black console window so that your keystrokes register inside the VM instead of your local computer.
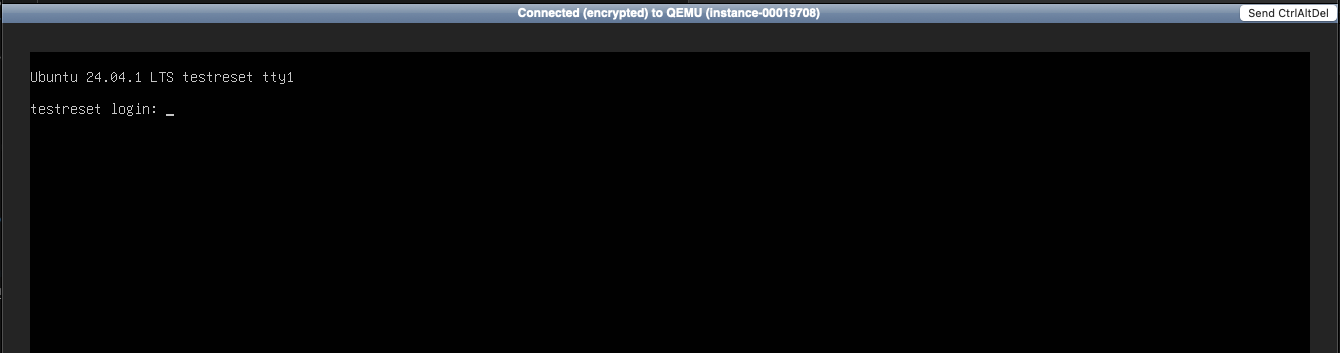
3. Reboot and enter GRUB¶
Click "Send CtrlAltDel". Immediately click inside the console window and press ESC repeatedly.
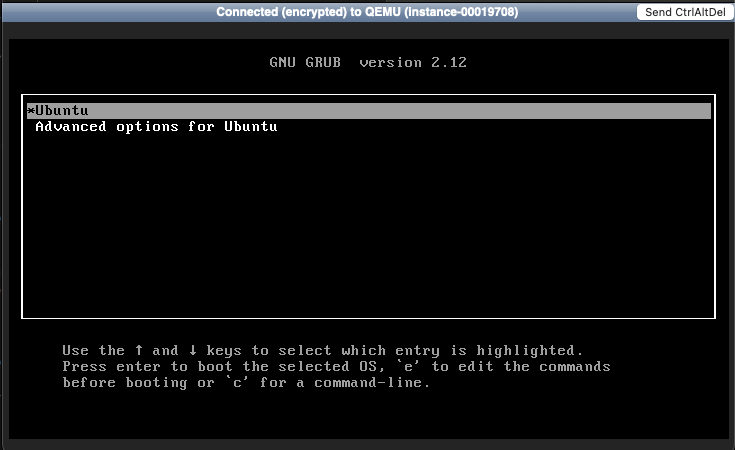
Because the VM reboots quickly, you must be very fast. You should see the following GNU GRUB window. If instead the system continues to boot, allow the VM to boot fully, then repeat this step until you see the GRUB prompt after repeatedly pressing the ESC key.
 ¶
¶
4. Edit the boot entry¶
If you see the GNU GRUB boot menu, use the arrow keys to select the default boot entry (usually Ubuntu).
Press e to edit it.
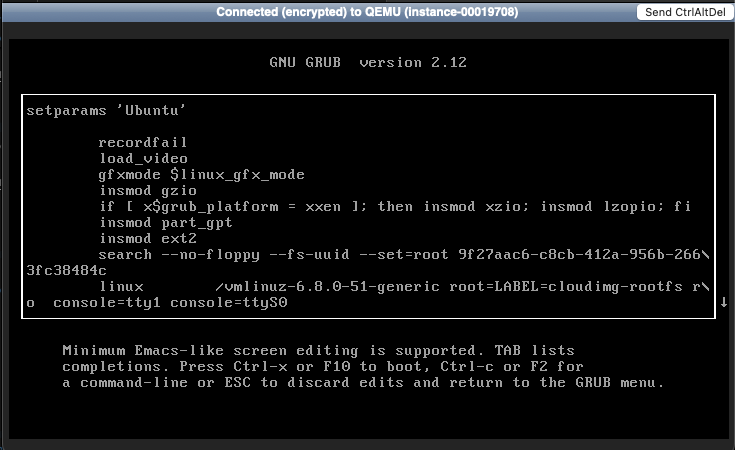
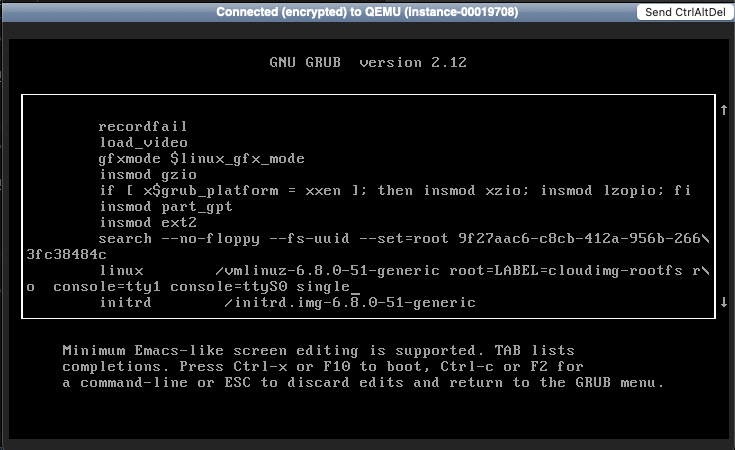
5. Add single-user mode¶
Scroll to the line that begins with linux.
At the end of the line, add the word single
6. Boot into maintenance mode¶
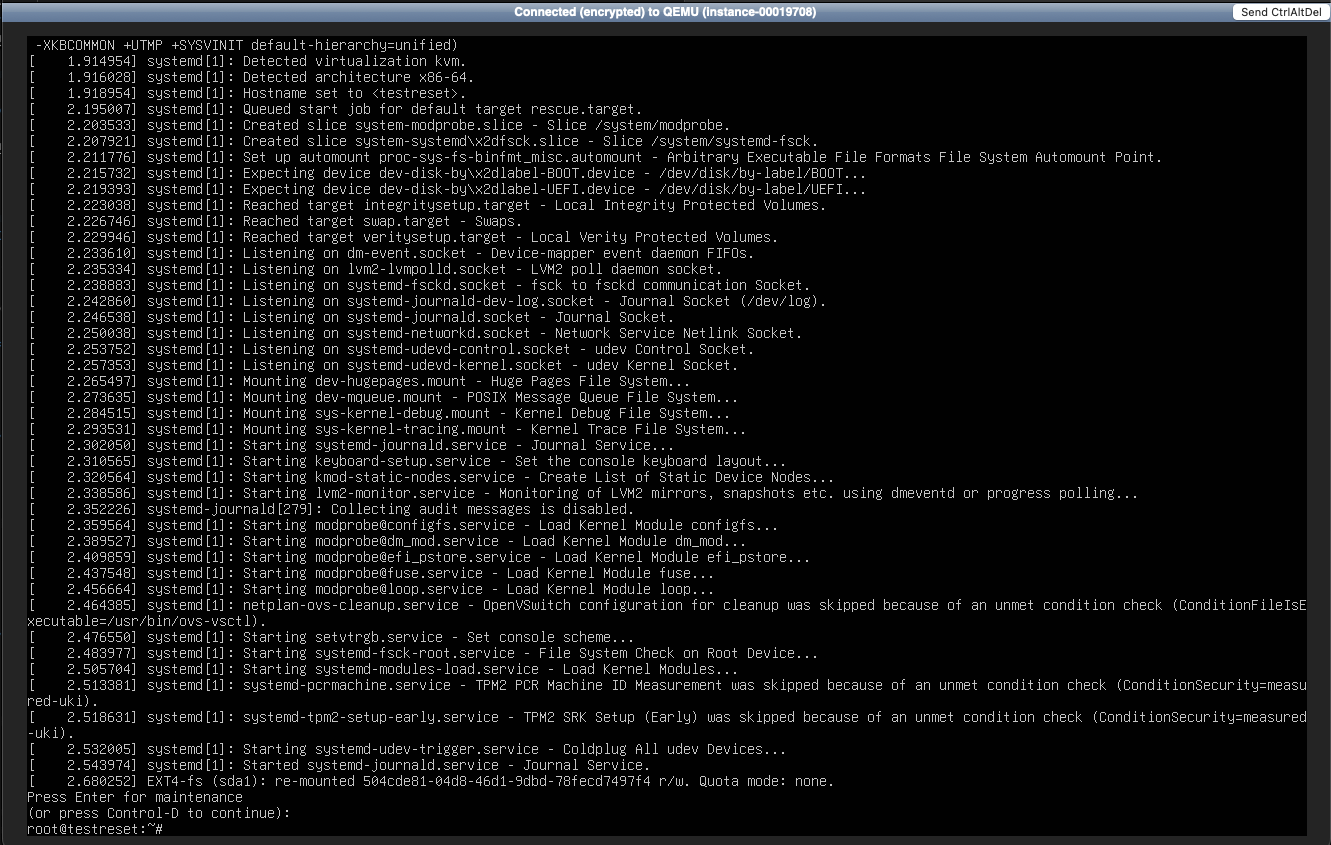
Press Ctrl+X to boot with the modified entry.
The system will begin to boot, and you should eventually see:
Press Enter, and you will be given a root shell prompt.
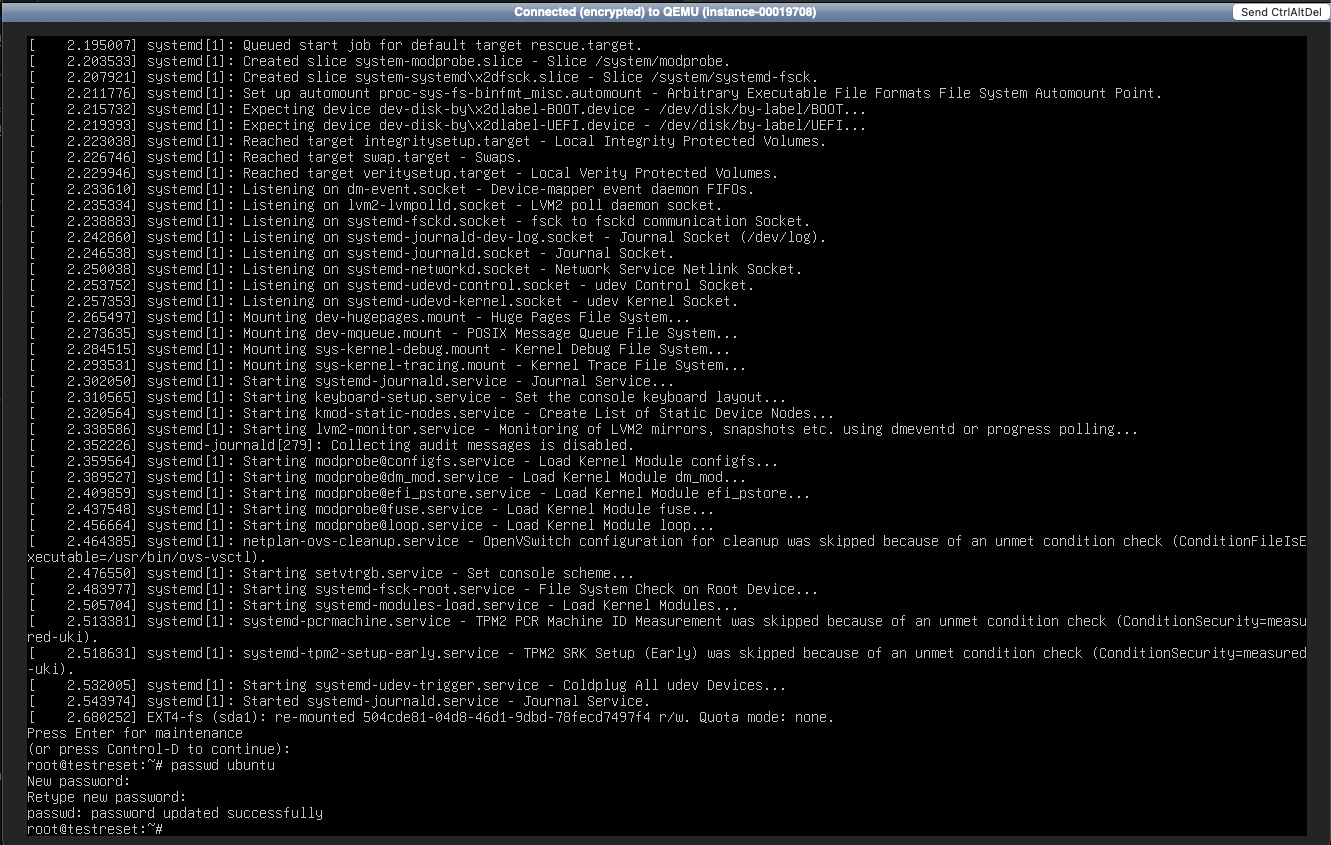
7. Reset a password¶
At the prompt, type:
This resets the password for the ubuntu user.
You may also reset the password for root or any other user as needed.
8. Exit maintenance mode¶
Type:
Your system should now continue booting to the normal login console.
9. Access with password or SSH¶
- If you normally use password-based access (not recommended), you can now log in with the new password using your normal processes.
- If you are using SSH key-based access (preferred), you will need to continue passed this step to also update your SSH key configuration.
10. Reset SSH key access¶
SSH keys are stored in:
To update them:
- First, log in with your new password via SSH.
- Edit the
authorized_keysfile to add your new SSH key.
⚠️ Since the web console does not allow cut-and-paste, this step is easiest to complete over an SSH session.
If your system is not configured to allow password login over SSH, you will need to temporarily enable it. For the Rumble Cloud Ubuntu image, follow the instructions below. For other distributions the file location, etc. may be slightly different.:
-
Edit:
Set: -
Restart SSH:
11. Revert Temporary Changes¶
After you confirm SSH key access is restored:
- Revert the SSH configuration change (
PasswordAuthentication no). - Optionally remove the password you set earlier by running:
Troubleshooting¶
GRUB does not appear¶
- Ensure you are pressing ESC repeatedly right after sending CtrlAltDel.
- If the console does not capture your key presses, click inside the console window immediately after pressing Send CtrlAltDel.
System boots without maintenance prompt¶
- Double-check that you edited the correct
linuxline in GRUB. - Ensure the word
singlewas added at the very end of the line.
SSH keys get overwritten after reboot¶
Some images may have cloud-init enabled, which can overwrite ~/.ssh/authorized_keys on reboot.
To prevent this, edit:
and disablessh_deletekeys or other SSH-related options.
Cannot edit files in console¶
- The web console does not allow copy-paste. If you need to add long SSH keys, use password login temporarily, then update your key via an SSH session.
Summary¶
By following these steps, you can recover access to your Rumble Cloud VM when password or SSH key access is lost. The process leverages standard Linux recovery workflows, meaning it works the same way as it would on a physical linux server.